Canis lupus pallipes
Canis lupus pallipes

Crédit image:
licence CC BY 2.0 🛈
Trois individus.
Statut CITES
Canis lupus pallipes, le Loup des Indes, est une sous-espèce de Canis lupus vivant en Inde et au Moyen-Orient.
Répartition
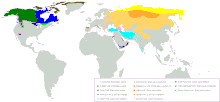

L'aire de répartition de cette sous-espèce recouvre l'Inde et le Moyen-Orient[1]
Systématique
Cette sous-espèce est décrite par le zoologiste britannique William Henry Sykes, en 1831[2].
Ce taxon porte en français le nom vernaculaire ou normalisé « Loup des Indes »[3]. À ne pas confondre avec Canis indica qui serait une espèce à part entière comme le montre l'étude (notamment sur l'ARNr 16S) de Aggarwal, Kivisild, Ramadevi & Singh en 2007[4].
Notes et références
- ↑ GBIF Secretariat. GBIF Backbone Taxonomy. Checklist dataset https://doi.org/10.15468/39omei accessed via GBIF.org, consulté le 24 octobre 2021.
- ↑ (en) William Henry Sykes, Proceedings of the Committee of Science and Correspondence of the Zoological Society of London, (lire en ligne), p. 101
- ↑ (en) « Canis lupus pallipes Sykes, 1831 : Names », sur www.speciesplus.net (consulté le )
- ↑ (en) R. K. Aggarwal, T. Kivisild, J. Ramadevi et L. Singh, « Mitochondrial DNA coding region sequences support the phylogenetic distinction of two Indian wolf species », Journal of Zoological Systematics and Evolutionary Research, vol. 45, no 2, , p. 163–172 (ISSN 1439-0469, DOI 10.1111/j.1439-0469.2006.00400.x, lire en ligne, consulté le )
Voir aussi
Bibliographie
- (en) M. Singh et H. N. Kumara, « Distribution, status and conservation of Indian gray wolf (Canis lupus pallipes) in Karnataka, India », Journal of Zoology, Wiley-Blackwell, vol. 0, no 0, , p. 060606025751017-??? (ISSN 1469-7998, 0022-5460 et 0952-8369, OCLC 15264754, DOI 10.1111/J.1469-7998.2006.00103.X).
- (en) Rasoul Khosravi, Hamid-Reza Rezaei et Mohammad Kaboli, « Detecting hybridization between Iranian wild wolf (Canis lupus pallipes) and free-ranging domestic dog (Canis familiaris) by analysis of microsatellite markers », Zoological Science, Zoological Society of Japan (), vol. 30, no 1, , p. 27-34 (ISSN 0289-0003 et 2212-3830, OCLC 51963016, PMID 23317363, DOI 10.2108/ZSJ.30.27).
- (en) Sanath Krishna Muliya, Arun A Shanmugam, Pa Kalaignan, Linto Antony, Harikrishnan Chandranpillai et Nirupama Jaisingh, « Chemical immobilisation of dhole (Cuon alpinus), Indian jackal (Canis aureus indicus) and Indian wolf (Canis lupus pallipes) with ketamine hydrochloride-xylazine hydrochloride », Veterinary medicine and science, Wiley-Blackwell et Wiley, vol. 2, no 3, , p. 221-225 (ISSN 2053-1095, PMID 29067197, PMCID 5645868, DOI 10.1002/VMS3.35).
- (en) Lalit K Sharma, Tanoy Mukherjee, Phakir Chandra Saren et Kailash Chandra, « Identifying suitable habitat and corridors for Indian Grey Wolf (Canis lupus pallipes) in Chotta Nagpur Plateau and Lower Gangetic Planes: A species with differential management needs », PLOS One, PLoS, vol. 14, no 4, , e0215019 (ISSN 1932-6203, OCLC 228234657, PMID 30969994, PMCID 6457547, DOI 10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0215019).
- (en) Sougata Sadhukhan, Lauren Hennelly et Bilal Habib, « Characterising the harmonic vocal repertoire of the Indian wolf (Canis lupus pallipes) », PLOS One, PLoS, vol. 14, no 10, , e0216186 (ISSN 1932-6203, OCLC 228234657, PMID 31671161, PMCID 6822943, DOI 10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0216186).
Liens externes
- (en) BioLib : Canis lupus pallipes Sykes, 1831 (consulté le )
- (en) Catalogue of Life : Canis lupus pallipes Sykes, 1831 (consulté le )
- (en) CITES : Canis lupus pallipes Sykes, 1831 (+ répartition sur Species+) (consulté le )
- (fr + en) EOL : Canis lupus pallipes Sykes 1831 (consulté le )
- (fr + en) GBIF : Canis lupus subsp. pallipes Sykes, 1831 (consulté le )
- (fr + en) ITIS : Canis lupus pallipes Sykes, 1831 (consulté le )
- (en) Mammal Species of the World (3e éd., 2005) : Canis lupus pallipes Sykes, 1831 (consulté le )
- (en) NCBI : Canis lupus pallipes Sykes, 1831 (taxons inclus) (consulté le )
- (en) Taxonomicon : Canis lupus pallipes Sykes, 1831 (consulté le )

